Standing up to bullies was once a brave act that defied social norms. Today, the landscape is not so clear-cut. Enter: cyberbullying. Adolescents are forced to endure online harassment from peers at any given hour of the day — often without even knowing the identity of the bully. The prevalence of digital devices has created a pressing health problem for the world’s youth that’s not limited to school grounds.
In this post, we shed light on 15 of the most alarming cyberbullying statistics that show how dangerous online harassment can be. They cover the root causes and effects of online bullying, where cyberbullying is most prevalent and, most importantly, how to detect online bullying and what to do about it.
Table of Contents:
What Is Cyberbullying?
Cyberbullying is the use of electronic communication to bully a person, typically by sending intimidating or threatening messages. It can happen through social media, text messages, online chats and websites.
Here are some of the common examples of cyberbullying:
- Sharing embarrassing photos or videos of someone online without their permission
- Sending mean or threatening messages
- Spreading rumors about someone online
- Excluding someone from online groups
General Cyberbullying Statistics
Cyberbullying is a significant issue affecting children, adolescents and adults. It’s prevalent across various online platforms and can target individuals based on their physical appearance, personality, gender, race or ethnicity.
1. Forty-six percent of U.S. teens report experiencing some form of cyberbullying (Pew Research Center)
2. More than half (54%) of adolescent girls have experienced cyberbullying in their lifetimes. (Pew Research Center)
3. Fifty-eight percent of netizens say that hate speech is most widespread on Facebook. (Ipsos)
4. Forty-nine percent of 15-to-17-year-olds have experienced online harassment. (Pew Research Center)
5. About 1 in 5 cyberbullied teens say they were targeted because of their gender (22%) or racial/ethnic background (20%). (Pew Research Center)
6. Sixty-seven percent of internet users have encountered hate speech online, including 74% of those under 35. (Ipsos)

Cyberbullying in School Statistics
Cyberbullying within schools is a widespread concern, impacting students’ well-being and academic performance. Monitoring social media activity and implementing comprehensive prevention strategies are essential in addressing this issue.
7. Thirty percent of teenagers believe that school districts monitoring students’ social media activity for bullying or harassment would be highly beneficial. (Pew Research Center)
8. About 27% of students said they had been cyberbullied in the most recent 30 days. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
9. Fifty-five percent of students reported experiencing cyberbullying at some point in their lives. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
10. When asked about cyberbullying in the past 30 days, students most commonly reported mean or hurtful comments online (30.4%), exclusion from group chats (28.9%), rumors spread online (28.4%) and online embarrassment or humiliation (26.9%). (Cyberbullying Research Center)
11. In a 2023 survey, 24.2% of boys and 28.6% of girls reported being cyberbullied within the last 30 days. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
12. More than 60% of students who encountered cyberbullying reported that it significantly impacted their learning and sense of safety at school. (Cyberbullying Research Center)
13. Ten percent of students admitted to skipping school at least once in the past year due to cyberbullying. (Cyberbullying Research Center)

Adult Cyberbullying Statistics
Cyberbullying isn’t limited to young people; adults also experience its harmful effects. It can lead to mental health issues such as depression and even suicide. Implementing effective prevention measures and promoting digital citizenship are crucial in combating cyberbullying across all age groups.
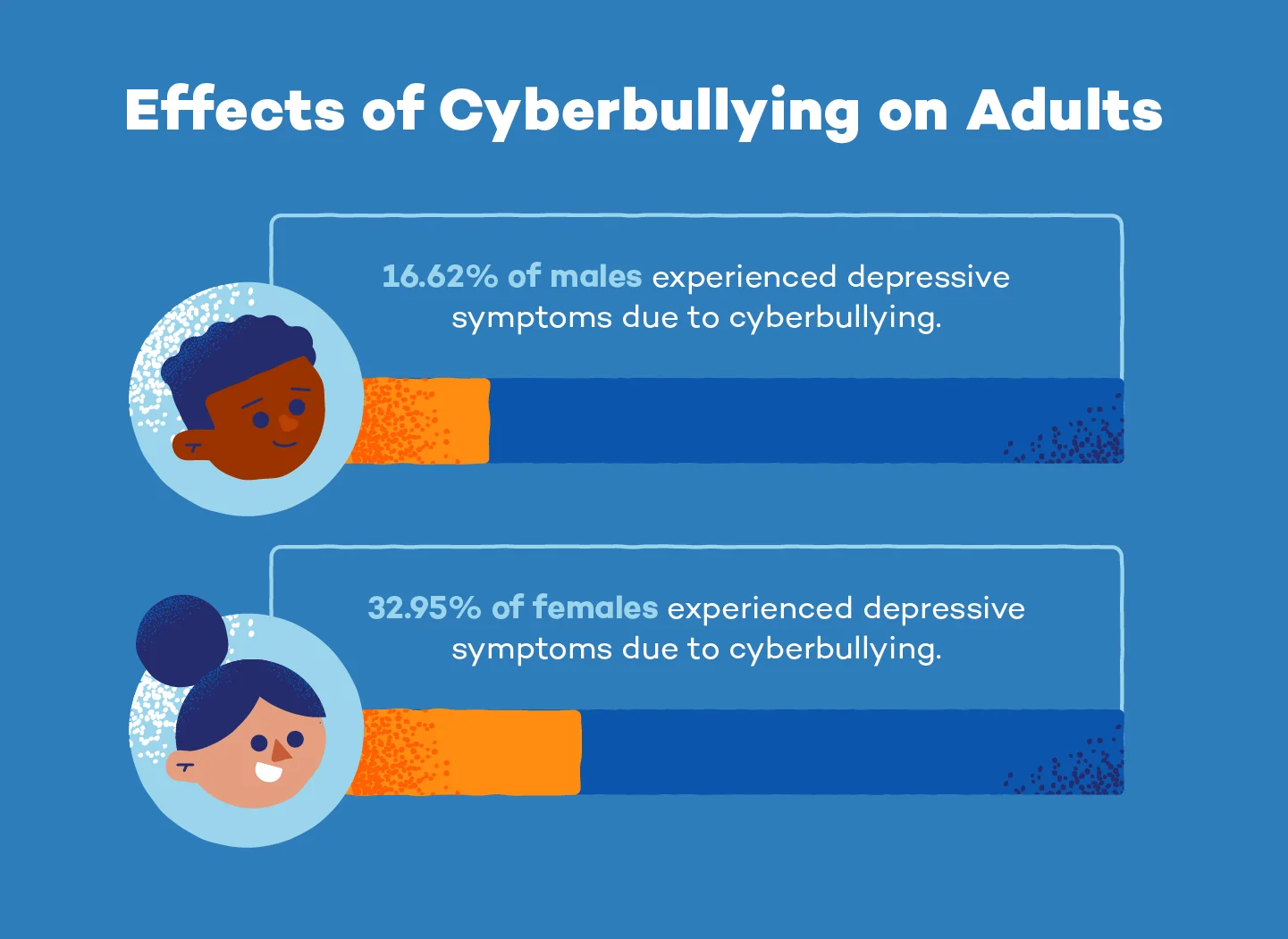
14. About 16.62% of males and 32.95% of females experienced depressive symptoms due to cyberbullying. (BMC Psychiatry)
15. About 7.54% of females and 2.3% of males seriously considered attempting suicide due to cyberbullying. (BMC Psychiatry)
How to Recognize and Prevent Online Bullying
It’s important to be aware of the types of cyberbullying to combat becoming one of the cybersecurity statistics. If you suspect your child is engaged in one or more of the following behaviors, it’s time to take action and protect your child from cyberbullying.
- Flaming: Online arguments that take place within DMs and messaging apps, oftentimes with vulgar behavior to provoke another person
- Harassment: Sending offensive messages repeatedly, including verbal abuse and unsolicited sexual content
- Denigration: Distributing derogatory or false information about someone to damage their reputation
- Cyberstalking: Repeatedly sending threatening messages in an attempt to intimidate someone; in some cases, this behavior is illegal
- Masquerade: Creating a fake account pretending to be someone else, sometimes even stealing credentials and posting embarrassing or vicious content
- Trolling: Baiting other users to fight online
Notable warning signs of cyberbullying can include withdrawing from social activities, avoiding school, dropping grades or appearing anxious or sad after going online. In some cases, cyberbullying is illegal. In less severe cases, blocking the perpetrator and contacting a school administrator is the best course of action. Be proactive as a parent — keep parental controls on and set a media agreement with your children.
Additional Resources
These cyberbullying prevention resources have additional information for suicide prevention, healthy technology habits and articles with practical parental advice.
Online bullying is a problem that will persist as technological advances continue. Be aware of your children’s internet use and download proper parental controls to handle and prevent cyberbullying effectively.
Cyberbullying FAQ
How Many Kids Get Cyberbullied Each Year?
In 2023, the Cyberbullying Research Center found that 55% of students between the ages of 13 and 17 have experienced cyberbullying in their lifetime.
Which Country Has the Highest Rate of Cyberbullying?
A survey found that about 28% of children worldwide have faced racially motivated cyberbullying, as reported by their parents, with the highest rates in India and the U.S.
What Age Group Has the Highest Rate of Cyberbullying?
The age group with the highest rate of cyberbullying tends to be adolescents and young adults, typically between 12 to 17 years old.
Which Social Media Platform Has the Highest Rate of Cyberbullying?
The most common special media platforms for cyberbullying are Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and Snapchat.