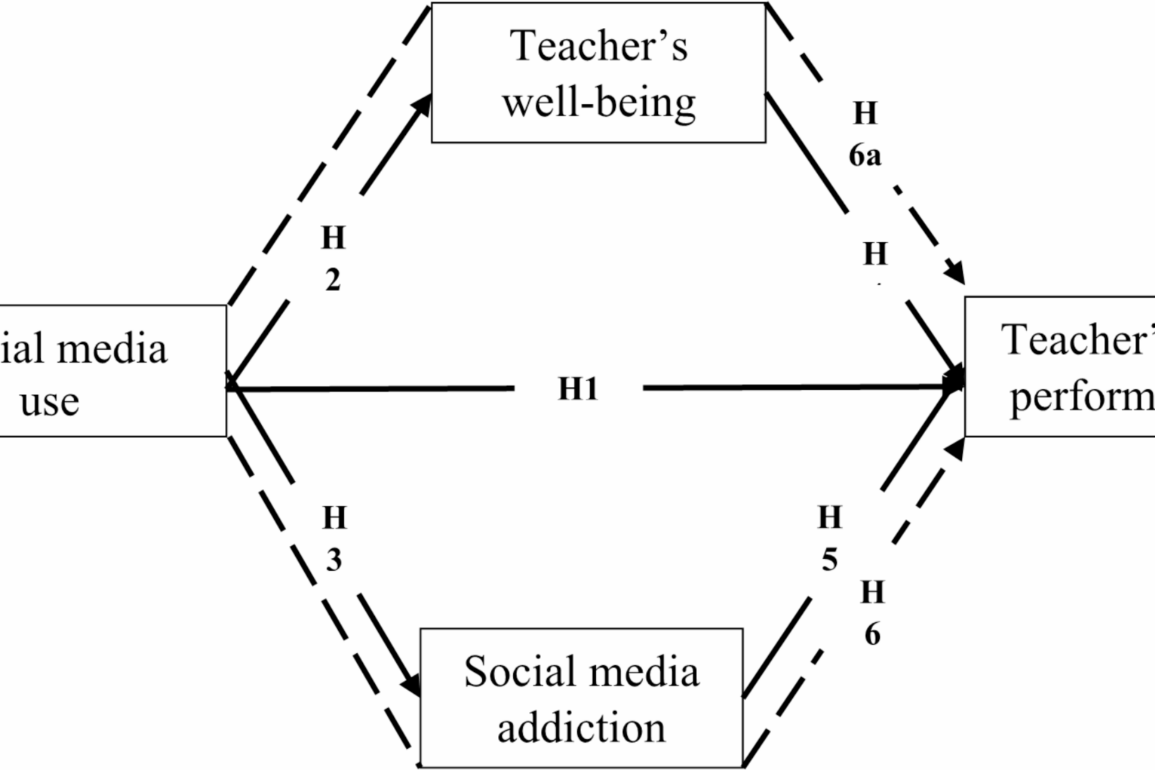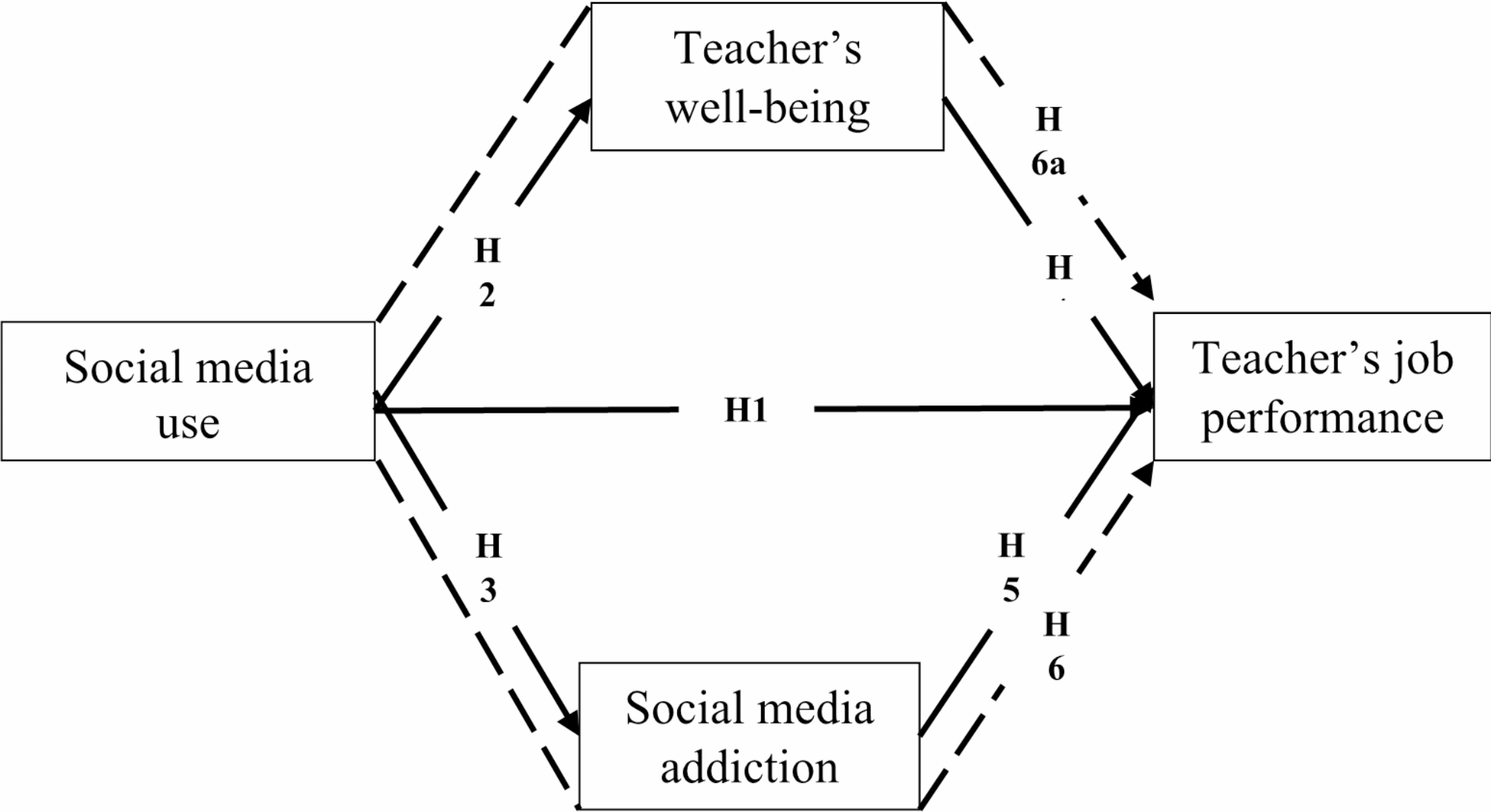
Lavy S, Ayuob W. Teachers’ Sense of Meaning Associations With Teacher Performance and Graduates’ Resilience: A Study of Schools Serving Students of Low Socio-Economic Status. Front Psychol 2019, 10.
Li M, Pérez-Díaz PA, Mao Y, Petrides KV. A Multilevel Model of Teachers’ Job Performance: Understanding the Effects of Trait Emotional Intelligence, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Trust. Front Psychol 2018, 9.
Chamizo-Nieto MT, Arrivillaga C, Rey L, Extremera N. The Role of Emotional Intelligence, the Teacher-Student Relationship, and Flourishing on Academic Performance in Adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Study. Front Psychol 2021, 12.
Harris SP, Davies RS, Christensen SS, Hanks J, Bowles B. Teacher Attrition: Differences in Stakeholder Perceptions of Teacher Work Conditions. Educ Sci 2019, 9(4).
Yang Y, Li G, Su Z, Yuan Y. Teacher’s Emotional Support and Math Performance: The Chain Mediating Effect of Academic Self-Efficacy and Math Behavioral Engagement. Front Psychol 2021, 12.
Balakrishnan SR, Soundararajan V, Parayitam S. Recognition and rewards as moderators in the relationships between antecedents and performance of women teachers: evidence from India. International Journal of Educational Management 2022, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print)
Akhtar S, Khan KU, Hassan S, Irfan M, Atlas F. Antecedents of task performance: An examination of transformation leadership, team communication, team creativity, and team trust. J Public Affairs. 2019;19(2):e1927.
Shi Y, Yu H, Di S, Ma C. Body Mass Index and Academic Achievement Among Chinese Secondary School Students: The Mediating Effect of Inhibitory Control and the Moderating Effect of Social Support. Front Psychol 2022, 13.
Qalati SA, Ostic D, Sulaiman MABA, Gopang AA, Khan A. Social Media and SMEs’ Performance in Developing Countries: Effects of Technological-Organizational-Environmental Factors on the Adoption of Social Media. SAGE Open. 2022;12(2):21582440221094594.
Fan M, Qalati SA, Khan MAS, Shah SMM, Ramzan M, Khan RS. Effects of entrepreneurial orientation on social media adoption and SME performance: The moderating role of innovation capabilities. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(4):e0247320.
Pekkala K, van Zoonen W. Work-related social media use: The mediating role of social media communication self-efficacy. Eur Manag J. 2022;40(1):67–76.
Qalati SA, Ostic D, Shuibin G, Mingyue F. A mediated–moderated model for social media adoption and small and medium-sized enterprise performance in emerging countries. Manag Decis Econ. 2022;43(3):846–61.
Liu Y, Bakici T. Enterprise social media usage: The motives and the moderating role of public social media experience. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;101:163–72.
Landers RN, Schmidt GB. Social Media in Employee Selection and Recruitment: An Overview. In: Social Media in Employee Selection and Recruitment: Theory, Practice, and Current Challenges. edn. Edited by Landers RN, Schmidt GB. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2016: 3–11.
Aldahdouh TZ, Nokelainen P, Korhonen V. Technology and Social Media Usage in Higher Education: The Influence of Individual Innovativeness. SAGE Open. 2020;10(1):2158244019899441.
Wang X, Zhang R, Wang X, Xu D, Tian F. How Do Mobile Social Apps Matter for College Students’ Satisfaction in Group-Based Learning? The Mediation of Collaborative Learning. Front Psychol 2022, 13.
Jiang Y. Problematic Social Media Usage and Anxiety Among University Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Role of Psychological Capital and the Moderating Role of Academic Burnout. Front Psychol 2021, 12.
Yang C-c, Holden SM, Ariati J. Social Media and Psychological Well-Being Among Youth: The Multidimensional Model of Social Media Use. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2021;24(3):631–50.
Ostic D, Qalati SA, Barbosa B, Shah SMM, Galvan Vela E, Herzallah AM, Liu F. Effects of Social Media Use on Psychological Well-Being: A Mediated Model. Front Psychol 2021, 12.
Luqman A, Talwar S, Masood A, Dhir A. Does enterprise social media use promote employee creativity and well-being? J Bus Res. 2021;131:40–54.
Louati H, Hadoussa S. Study of Social media impacts on social capital and employee performance – evidence from Tunisia Telecom. J Decis Syst. 2021;30(2–3):118–49.
Yang X, Ye H, Wang X. Social media use and work efficiency: Insights from the theory of communication visibility. Inf Manag. 2021;58(4):103462.
Bouffard S, Giglio D, Zheng Z. Social Media and Romantic Relationship: Excessive Social Media Use Leads to Relationship Conflicts, Negative Outcomes, and Addiction via Mediated Pathways. Social Sci Comput Rev 2021:08944393211013566.
Labban A, Bizzi L. Are social media good or bad for employees? It depends on when they use them. Behav Inform Technol. 2022;41(4):678–93.
Zimmer JC. Problematic social network use: Its antecedents and impact upon classroom performance. Comput Educ. 2022;177:104368.
Moqbel M, Kock N. Unveiling the dark side of social networking sites: Personal and work-related consequences of social networking site addiction. Inf Manag. 2018;55(1):109–19.
Bandura AJAp. The self system in reciprocal determinism. 1978, 33(4):344.
Bandura A. Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall; 1986.
Fang GG, Qalati SA, Ostic D, Shah SMM, Mirani MA. Effects of entrepreneurial orientation, social media, and innovation capabilities on SME performance in emerging countries: a mediated–moderated model. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 2021:1–13.
Cao X, Ali A. Enhancing team creative performance through social media and transactive memory system. Int J Inf Manag. 2018;39:69–79.
Cao X, Yu L. Exploring the influence of excessive social media use at work: A three-dimension usage perspective. Int J Inf Manag. 2019;46:83–92.
Al-Rahmi WM, Alias N, Othman MS, Marin VI, Tur G. A model of factors affecting learning performance through the use of social media in Malaysian higher education. Comput Educ. 2018;121:59–72.
Jafar RMS, Geng S, Ahmad W, Niu B, Chan FTS. Social media usage and employee’s job performance. Industrial Manage Data Syst. 2019;119(9):1908–25.
Zachos G, Paraskevopoulou-Kollia E-A, Anagnostopoulos I. Social Media Use in Higher Education: A Review. Educ Sci 2018, 8(4).
Best P, Manktelow R, Taylor B. Online communication, social media and adolescent wellbeing: A systematic narrative review. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2014;41:27–36.
Panadero E, Fraile J, Pinedo L, Rodríguez-Hernández C, Balerdi E, Díez F. Teachers’ Well-Being, Emotions, and Motivation During Emergency Remote Teaching Due to COVID-19. Front Psychol 2022, 13.
Chan M-k, Sharkey JD, Lawrie SI, Arch DAN, Nylund-Gibson K. Elementary school teacher well-being and supportive measures amid COVID-19: An exploratory study. Educational Publishing Foundation; 2021: 533–45.
Alves R, Lopes T, Precioso J. Teachers’ well-being in times of Covid-19 pandemic: factors that explain professional well-being. IJERI: Int J Educational Res Innov. 2020;15:203–17.
Jennings PA. Early Childhood Teachers’ Well-Being, Mindfulness, and Self-Compassion in Relation to Classroom Quality and Attitudes Towards Challenging Students. Mindfulness. 2015;6(4):732–43.
Tkáčová H, Pavlíková M, Jenisová Z, Maturkanič P, Králik R. Social Media and Students’ Wellbeing: An Empirical Analysis during the Covid-19 Pandemic. Sustainability. 2021;13(18):10442.
van Zoonen W, Treem JW, ter Hoeven CL. A tool and a tyrant: Social media and well-being in organizational contexts. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022;45:101300.
Valkenburg PM, van Driel II, Beyens I. The associations of active and passive social media use with well-being: A critical scoping review. New Media Soc. 2021;24(2):530–49.
O’Reilly M, Dogra N, Whiteman N, Hughes J, Eruyar S, Reilly P. Is social media bad for mental health and wellbeing? Exploring the perspectives of adolescents. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;23(4):601–13.
Majid A, Yasir M, Javed A, Ali P. From envy to social anxiety and rumination: How social media site addiction triggers task distraction amongst nurses. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2020;28(3):504–13.
Simons M, Reijnders J, Peeters S, Janssens M, Lataster J, Jacobs N. Social network sites as a means to support personal social capital and well-being in older age: An association study. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;3:100067.
Wang T, Wong JYH, Wang MP, Li ACY, Kim SS, Lee JJ. Effects of Social Networking Service (SNS) Addiction on Mental Health Status in Chinese University Students: Structural Equation Modeling Approach Using a Cross-sectional Online Survey. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(12):e26733.
Alotaibi MS, Fox M, Coman R, Ratan ZA, Hosseinzadeh H. Smartphone Addiction Prevalence and Its Association on Academic Performance, Physical Health, and Mental Well-Being among University Students in Umm Al-Qura University (UQU), Saudi Arabia. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(6).
Zhang Y, Mei S, Li L, Chai J, Li J, Du H. The Relationship between Impulsivity and Internet Addiction in Chinese College Students: A Moderated Mediation Analysis of Meaning in Life and Self-Esteem. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0131597.
Isham A, Mair S, Jackson T. Worker wellbeing and productivity in advanced economies: Re-examining the link. Ecol Econ. 2021;184:106989.
Isham A, Mair S, Jackson T. Wellbeing and productivity: a review of the literature. 2020.
Krekel C, Ward G, De Neve JE. Employee wellbeing, productivity, and firm performance. Saïd Bus School WP 2019, 4.
Pagán-Castaño E, Maseda-Moreno A, Santos-Rojo C. Wellbeing in work environments. J Bus Res. 2020;115:469–74.
Abdullah MI, Huang D, Sarfraz M, Ivascu L, Riaz A. Effects of internal service quality on nurses’ job satisfaction, commitment and performance: Mediating role of employee well-being. Nurs Open. 2021;8(2):607–19.
Díaz-García GA, Ortiz-de-Urbina-Criado M, Ravina-Ripoll R. Happy leadership, now more than ever. Int J Happiness Dev. 2024;8(3):223–43.
Song JH, Chai DS, Kim J, Bae SH. Job Performance in the Learning Organization: The Mediating Impacts of Self-Efficacy and Work Engagement. Perform Improv Q. 2018;30(4):249–71.
Swanson E, Kim S, Lee S-M, Yang J-J, Lee Y-K. The effect of leader competencies on knowledge sharing and job performance: Social capital theory. J Hospitality Tourism Manage. 2020;42:88–96.
Yingjie L, Deng S, Pan T. Does usage of enterprise social media affect employee turnover? Empirical evidence from Chinese companies. Internet Res. 2019;29(4):970–92.
Javed A, Yasir M, Majid A, Shah HA, Islam Eu, Asad S, Khan MW. Evaluating the effects of social networking sites addiction, task distraction, and self-management on nurses’ performance. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(11):2820–33.
Zivnuska S, Carlson JR, Carlson DS, Harris RB, Harris KJ. Social media addiction and social media reactions: The implications for job performance. J Soc Psychol. 2019;159(6):746–60.
Karaiskos D, Tzavellas E, Balta G, Paparrigopoulos T. P02-232 – Social Network Addiction: a New Clinical Disorder? Eur Psychiatry. 2010;25(S1):1–1.
Andreassen CS, Torsheim T, Pallesen S. Use of Online Social Network Sites for Personal Purposes at Work: Does it Impair Self-Reported Performance? Compr Psychol. 2014;3(01):21–CP. 03.18.
Rasool SF, Wang M, Tang M, Saeed A, Iqbal J. How Toxic Workplace Environment Effects the Employee Engagement: The Mediating Role of Organizational Support and Employee Wellbeing. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18(5).
Hoque KE, Bt Kenayathulla HB, D/O Subramaniam MV, Islam R. Relationships Between Supervision and Teachers’ Performance and Attitude in Secondary Schools in Malaysia. SAGE Open. 2020;10(2):2158244020925501.
Emerson RW. Convenience Sampling, Random Sampling, and Snowball Sampling: How Does Sampling Affect the Validity of Research? J Visual Impairment Blindness. 2015;109(2):164–8.
Yiming L, Yan L, Jinsheng Z. Effects of organizational climate on employee job satisfaction and psychological well-being: the role of technological influence in Chinese higher education. BMC Psychol. 2024;12(1):536.
Qalati SA, Ostic D, Fan M, Dakhan SA, Vela EG, Zufar Z, Sohu JM, Mei J, Thuy TTH. The General Public Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices Regarding COVID-19 During the Lockdown in Asian Developing Countries. Int Q Community Health Educ 2021:0272684X211004945.
Mei B, Brown GTL. Conducting Online Surveys in China. Social Sci Comput Rev. 2017;36(6):721–34.
Yu L, Cao X, Liu Z, Wang J. Excessive social media use at work. Inform Technol People. 2018;31(6):1091–112.
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Lee J-Y, Podsakoff NP. Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol. 2003;88(5):879.
Hair JF, Risher JJ, Sarstedt M, Ringle CM. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur Bus Rev. 2019;31(1):2–24.
Kono S, Sato M. The potentials of partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) in leisure research. J Leisure Res 2022:1–21.
Riady Y, Alqahtany TM, Habibi A, Sofyan S, Albelbisi NA. Factors affecting teachers’ social media use during covid-19. Cogent Social Sci. 2022;8(1):2115658.
Guillén-Gámez FD, Ruiz-Palmero J, García MG. Digital competence of teachers in the use of ICT for research work: development of an instrument from a PLS-SEM approach. Educ Inform Technol. 2023;28(12):16509–29.
Qalati SA, Siddiqui F, Magni D. Senior management’s sustainability commitment and environmental performance: Revealing the role of green human resource management practices. Business Strategy and the Environment 2024, n/a(n/a).
Cao S, Xu P, Qalati SA, Wu K. Impact of Employee Environmental Concerns on Sustainable Practices: Investigating Organizational Commitment and Job Satisfaction. In: Sustainability 16; 2024.
Qalati SA, Siddiqui F, Yusheng K. Linking consumer attitude with purchasing behavior via interpersonal influences: the role of corporate social responsibility. J Contemp Mark Sci. 2024;7(2):184–99.
Fan M, Ezeudoka BC, Qalati SA. Exploring the resistance to e-health services in Nigeria: an integrative model based upon the theory of planned behavior and stimulus-organism-response. Humanit Social Sci Commun. 2024;11(1):571.
Robina-Ramírez R, Ravina-Ripoll R, Castellano-Álvarez FJ. The trinomial health, safety and happiness promote rural tourism. BMC Public Health. 2023;23(1):1177.
Monecke A, Leisch F. semPLS: Structural Equation Modeling Using Partial Least Squares. J Stat Softw. 2012;48(3):1–32.
Revicki D. Internal Consistency Reliability. In: Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research. edn. Edited by Michalos AC. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands; 2014: 3305–3306.
Krabbe PFM. Chap. 7 – Validity. In: The Measurement of Health and Health Status. edn. Edited by Krabbe PFM. San Diego: Academic Press; 2017: 113–134.
Fornell C, Larcker DF. Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics. J Mark Res. 1981;18(3):382–8.
Chin WW. The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Mod methods Bus Res. 1998;295(2):295–336.
Falk RF, Miller NB. A primer for soft modeling. University of Akron; 1992.
Hair J, Black W, Babin B, Anderson R. Confirmatory factor analysis. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed; Pearson Education, Inc: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA 2010:600–638.
Fan M, Huang Y, Qalati SA, Shah SMM, Ostic D, Pu Z. Effects of Information Overload, Communication Overload, and Inequality on Digital Distrust: A Cyber-Violence Behavior Mechanism. Front Psychol 2021, 12.
Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Personal Soc Psychol. 1986;51(6):1173.
MATTHEWS L, Hair J, MATTHEWS R. PLS-SEM: THE HOLY GRAIL FOR ADVANCED ANALYSIS. Mark Manage J 2018, 28(1).
Nitzl C, Roldan Jose L, Cepeda G. Mediation analysis in partial least squares path modeling: Helping researchers discuss more sophisticated models. Industrial Manage Data Syst. 2016;116(9):1849–64.