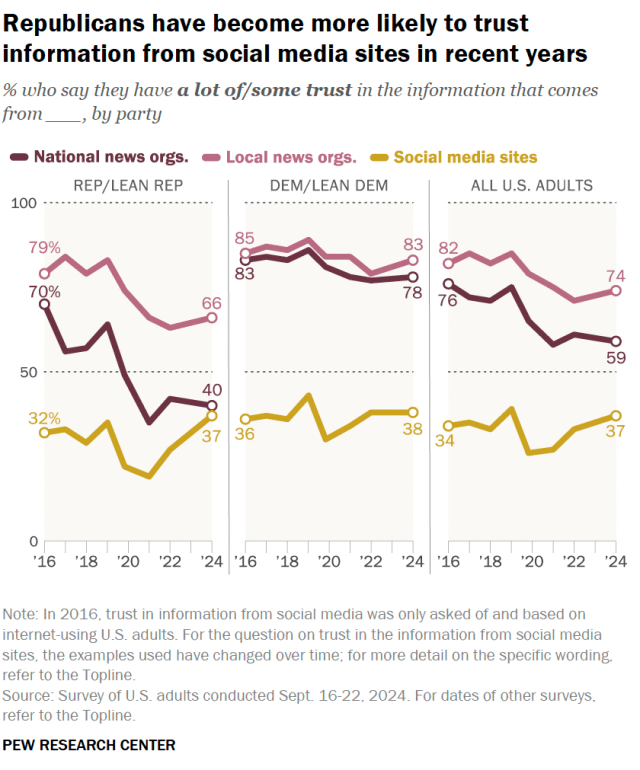
Republicans are now nearly as likely to trust the information that comes from social media sites as they are to trust information from national news organizations, according to a new Pew Research Center survey. The same pattern appears among young adults.
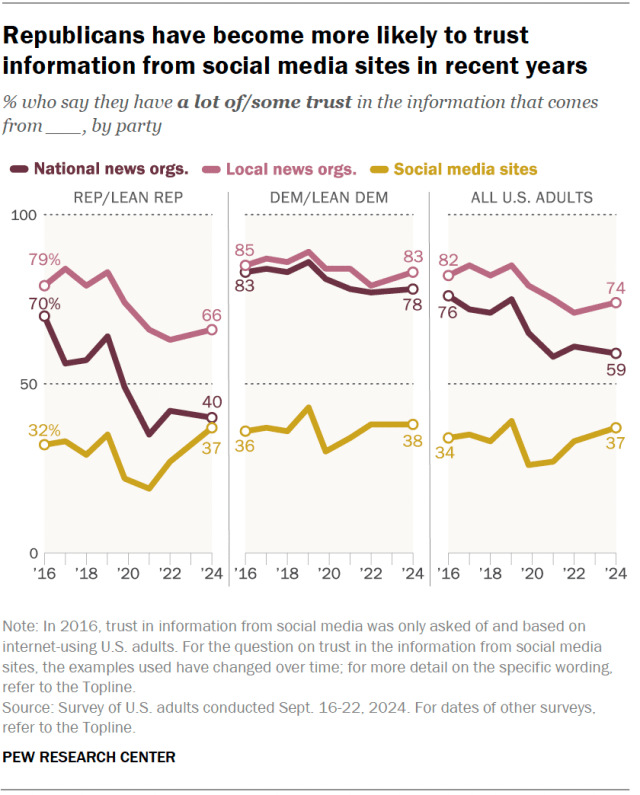
Today, 37% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents say they have a lot of or some trust in the information that comes from social media sites. This is nearly on par with the 40% of Republicans who express this level of trust in national news organizations. Their trust in national news outlets is now 30 percentage points lower than it was in 2016.
A much larger share of Republicans (66%) have at least some trust in information from local news organizations.
How we did this
This Pew Research Center analysis explores Americans’ trust in information from national and local news organizations as well as social media sites.
The survey of 9,680 U.S. adults was conducted from Sept. 16 to 22, 2024. Everyone who completed the survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), a group of people recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses who have agreed to take surveys regularly. This kind of recruitment gives nearly all U.S. adults a chance of selection. Surveys were conducted either online or by telephone with a live interviewer. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other factors. Read more about the ATP’s methodology.
Here are the questions used for this analysis, the topline and the survey methodology.
Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts, its primary funder. This is the latest analysis in Pew Research Center’s ongoing investigation of the state of news, information and journalism in the digital age, a research program funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts, with generous support from the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation.
Among Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, by comparison, 38% have at least some trust in the information that comes from social media sites. This is far below the share of Democrats who express this level of trust in information from national (78%) and local (83%) news organizations.
The share of Republicans who trust information from social media sites has increased notably since 2021, when just 19% trusted this type of information. Republicans have generally become less trusting of national and local news organizations in recent years. Democrats’ views have remained more consistent over time.
Young adults nearly as likely to trust social media as national news outlets
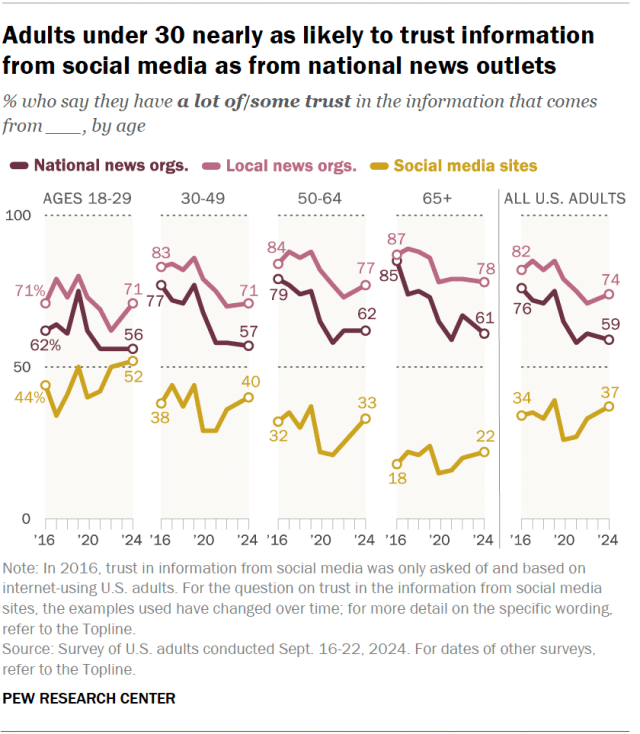
Across most age groups, Americans remain far less likely to trust information from social media sites than from national and local news organizations. But the youngest adults are an exception.
Adults under 30 are now nearly as likely to have a lot of or some trust in the information that comes from social media sites (52%) as from national news organizations (56%). More young adults (71%) express trust in information from local news outlets.
For all other age groups, trust in information from social media sites remains lower than trust in both local and national news organizations. The gap is especially large among the oldest Americans. Just 22% of those ages 65 and older say they have at least some trust in information from social media, compared with 61% who trust national news organizations and 78% who trust local news outlets.
Though trust in local news organizations has generally declined slightly since 2016, these remain the most-trusted news source across age groups – as they are across partisan groups.
Trust in information from news organizations varies by age and party
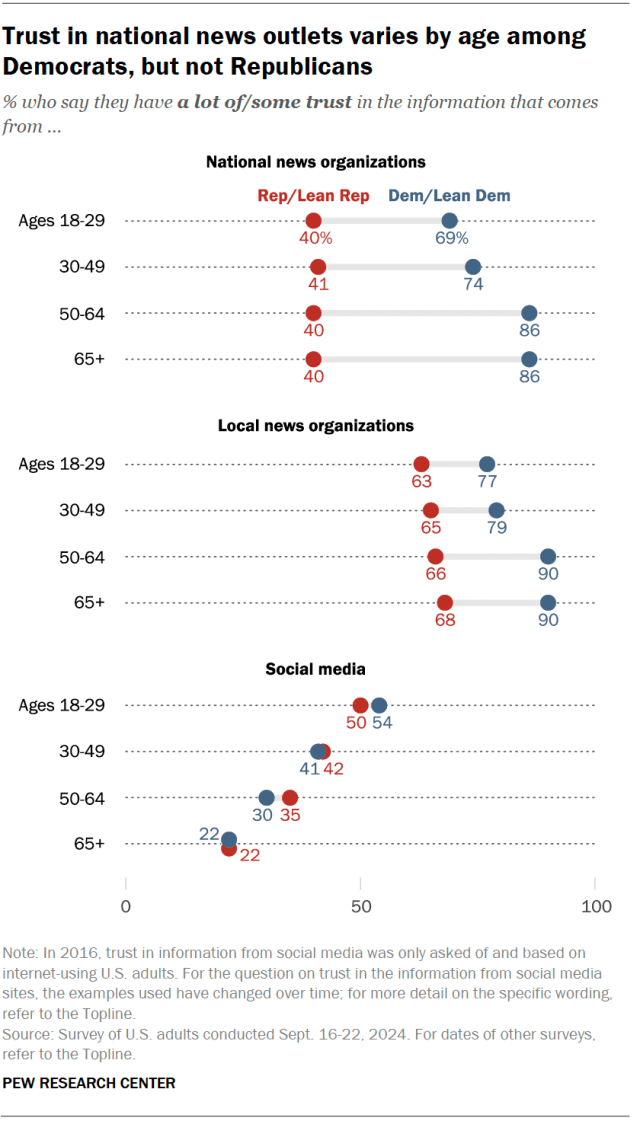
If partisanship was the only factor in Americans’ views toward national news organizations, one would expect young people to be more trusting, because young adults are more likely to be Democrats. But while there are few age differences in these views among Republicans, young Democrats are less likely than older Democrats to express trust in national news outlets.
Regardless of age group, around four-in-ten Republicans have a lot of or some trust in information from national news organizations. Democrats ages 50 and older, however, are much more likely than those under 30 to have at least some trust in national news outlets (86% vs. 69%).
Democrats ages 50 and older are also more likely than those under 30 to express trust in local news outlets (90% vs. 77%).
Conversely, younger adults – including both Democrats and Republicans – are more trusting than older adults of information from social media.
Note: This is an update of an analysis originally published on Oct. 27, 2022. Here are the questions used for this analysis, the topline and the survey methodology.
This post was originally published on this site be sure to check out more of their content